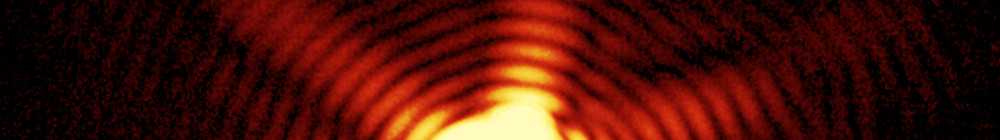
The American Physical Society (APS) selected our paper with the title “Three-Dimensional Reconstruction of the Giant Mimivirus Particle with an X-Ray Free-Electron Laser” (doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.114.098102) as highlight of the year 2015.
The American Physical Society (APS) selected our paper with the title “Three-Dimensional Reconstruction of the Giant Mimivirus Particle with an X-Ray Free-Electron Laser” (doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.114.098102) as highlight of the year 2015.
Author Archives: Max Hantke
X-ray imaging of a single virus in 3D
 Our paper with the title “Three-Dimensional Reconstruction of the Giant Mimivirus Particle with an X-Ray Free-Electron Laser” (doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.114.098102) has been published in the journal Physical Review Letters. The article is featured in a news item in Nature and as a viewpoint by APS Physics. For links to press releases and more articles covering our publication please go to the section Press.
Our paper with the title “Three-Dimensional Reconstruction of the Giant Mimivirus Particle with an X-Ray Free-Electron Laser” (doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.114.098102) has been published in the journal Physical Review Letters. The article is featured in a news item in Nature and as a viewpoint by APS Physics. For links to press releases and more articles covering our publication please go to the section Press.
BBC report: A look at the world’s most powerful X-ray laser
 The BBC reports about today’s most powerful X-ray laser, the LINAC coherent Light Source (LCLS) at Stanford University (California). Video
The BBC reports about today’s most powerful X-ray laser, the LINAC coherent Light Source (LCLS) at Stanford University (California). Video
Scientists Take First X-ray Portraits of Living Cyanobacteria at the LCLS
 Our article on “Imaging single cells in a beam of live cyanobacteria with an X-ray laser” (doi:10.1038/ncomms6704) has been published in Nature Communications. more...
Our article on “Imaging single cells in a beam of live cyanobacteria with an X-ray laser” (doi:10.1038/ncomms6704) has been published in Nature Communications. more...
Thousands of cell organelles imaged with an X-ray laser
 Our article with the title “High-throughput imaging of heterogeneous cell organelles with an X-ray laser” (doi:10.1038/nphoton.2014.270) has been published in Nature Photonics.
Our article with the title “High-throughput imaging of heterogeneous cell organelles with an X-ray laser” (doi:10.1038/nphoton.2014.270) has been published in Nature Photonics.
RACIRI Summer School 2014
 We are organising this year’s RACIRI Summer School under the title “Imaging with X-rays and Neutrons for Life and Materials Sciences”. It is held between 24 – 31 August 2014. The local venue is Skogshem Wijk in the Archiepelago of Stockholm.
We are organising this year’s RACIRI Summer School under the title “Imaging with X-rays and Neutrons for Life and Materials Sciences”. It is held between 24 – 31 August 2014. The local venue is Skogshem Wijk in the Archiepelago of Stockholm.
more…
Automated Classification
 Our article about “Automated identification and classification of single particle serial femtosecond X-ray diffraction data” (also known as “hit-finding”) has been published in Optics Express 22, pp 2497-2510 (2014). In an experiment which produced copious amounts of data, we use both algorithms analyzing diffraction images and time-of-flight spectroscopy to find when a particle is hit by the X-ray laser.
Our article about “Automated identification and classification of single particle serial femtosecond X-ray diffraction data” (also known as “hit-finding”) has been published in Optics Express 22, pp 2497-2510 (2014). In an experiment which produced copious amounts of data, we use both algorithms analyzing diffraction images and time-of-flight spectroscopy to find when a particle is hit by the X-ray laser.