X-ray lasers are creating new capabilities in understanding the structure of biological systems, complex materials and matter under extreme conditions. Extremely intense coherent X-ray pulses can be exploited to create and probe extreme states of matter, and also hold promise for structural determination of single macromolecules. We are involved in an inter-disciplinary research at the FLASH free-electron laser in Hamburg and the LCLS Linac Coherent Light Source in Stanford. We use the extremely short X-ray pulses to flash-image living cells, viruses, protein nanocrystals, and will ultimately investigate single protein macromolecules. All the samples exposed to these brilliant sources turn rapidly into plasma, offering us tantalizing possibilities to study fundamental physics problems in the high-energy density regime.
Here are a few of our recent projects with publications:
Atomic and molecular clusters in an X-ray laser beam
Explosion, ion acceleration, and molecular fragmentation of methane clusters in the pulsed beam of a free-electron laser, Bianca Iwan et al, Physical Review A 86 (2012) 033201.
DOI:10.1103/PhysRevA.86.033201
Explosions of xenon clusters in ultraintense femtosecond x-ray pulses from the LCLS free electron laser, Heiko Thomas et al., Physical Review Letters 108 (2012) 133401.
DOI:10.1103/PhysRevLett.108.133401
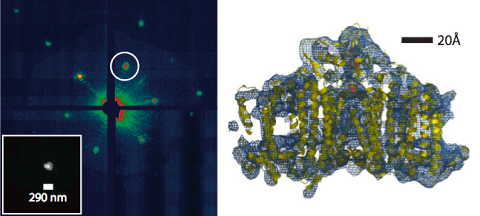
Biological particles in intense X-ray fields
Automated identification and classification of single particle serial femtosecond X-ray diffraction data, Jakob Andreasson et al, Optics Express 22 (2014) 2497
DOI:10.1364/OE.22.002497
Femtosecond diffractive imaging of biological cells, Marvin M. Seibert et al, Journal of Physics B – Atomic, molecular and optical physics 43 (2010) 194015.
DOI: 10.1088/0953-4075/43/19/194015
Feasibility of imaging living cells at sub-nanometer resolutions by utrafast X-ray diffraction
Magnus Bergh, Gösta Huldt, Nicusor Timneanu, Filipe Maia and Janos Hajdu,
Quarterly Reviews of Biophysics 41 (2008) 181.
DOI:10.1017/S003358350800471X
Femtosecond X-ray Protein Nanocrystallography
Self-terminating diffraction gates femtosecond X-ray nanocrystallography measurements,
Anton Barty et al., Nature Photonics 6 (2012) 35-40.
DOI:10.1038/nphoton.2011.297
Simulations of radiation damage in biomolecular nanocrystals induced by femtosecond X-ray pulses, Carl Caleman, Magnus Bergh, Howard A. Scott, John C. H. Spence, Henry N. Chapman and Nicusor Timneanu, Journal of Modern Optics 58 (2011) 1-12.
DOI: 10.1080/09500340.2011.597519
On the feasibility of nanocrystal imaging using intense and ultrashort 1.5 Å X-ray pulses,
Carl Caleman, Gösta Huldt, Carlos Ortiz, Filipe R. N. C. Maia, Fritz G. Parak, Janos Hajdu, David van der Spoel, Henry N. Chapman and Nicusor Timneanu, ACS Nano 5 (2011) 139-146.
DOI: 10.1021/nn1020693
Femtosecond X-ray protein nanocrystallography, Henry N. Chapman et al, Nature 470 (2011) 73-77.
DOI: 10.1038/nature09750
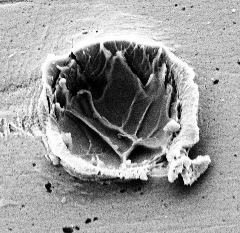
Ablation and ion acceleration from solids with X-ray lasers
Saturated ablation in metal hydrides and acceleration of protons and deuterons to keV energies with a soft x-ray laser, Jakob Andreasson et al, Physical Review E 83 (2011) 016403.
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevE.83.016403
TOF-OFF: A method for determining focal positions in tightly focused free-electron laser experiments by measurement of ejected ions, Bianca Iwan et al, High Energy Density Physics 7 (2011) 336-342.
DOI:10.1016/j.hedp.2011.06.008
Interaction of ultrashort X-ray pulses with B4C, SiC, and Si, Magnus Bergh, Nicusor Timneanu, Stefan P. Hau-Riege and Howard A. Scott, Physical Review E 77 (2008) 026404.
DOI:10.1103/PhysRevE.77.026404