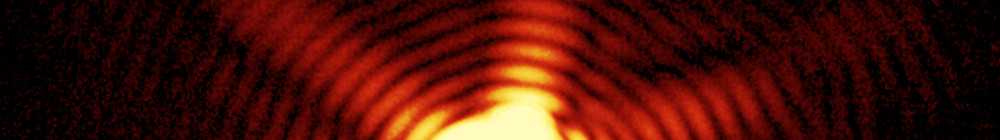
X-ray diffraction pattern generated from two different-sized spherical objects in close proximity to each other. © Nature Photonics
Ultrafast X-ray imaging on individual fragile specimens such as aerosols, metastable particles, superfluid quantum systems and live biospecimens provides high-resolution information that is inaccessible with conventional imaging techniques. Coherent X-ray diffractive imaging, however, suffers from intrinsic loss of phase, and therefore structure recovery is often complicated and not always uniquely defined. Here, we introduce the method of in-flight holography, where we use xenon or krypton nanoclusters as reference X-ray scatterers to encode relative phase information into diffraction patterns of a virus. The resulting hologram contains an unambiguous three-dimensional map of a virus and two nanoclusters with the highest lateral resolution so far achieved via single shot X-ray holography. Our approach unlocks the benefits of holography for ultrafast X-ray imaging of nanoscale, non-periodic systems and paves the way to direct observation of complex electron dynamics down to the attosecond timescale. This research was recently published in Nature Photonics.